Caesar Tonga oil field is located offshore in the Green Canyon area of the US Gulf of Mexico. Anadarko Petroleum holds 33.75% interest and is the operator of the oil field, while Equinor (formerly Statoil) and Chevron will hold 46% and 20.25% stakes, respectively.
Although Shell agreed to sell its 22.45% stake in the offshore field to Delek Group for $965m in April 2018, Equinor exercised its preferential rights to acquire Shell’s stake for the same amount in May 2019.
Further, the operator Anadarko Petroleum entered a definitive merger agreement with Occidental Petroleum in May 2019. Occidental Petroleum will be the designated operator of the Caesar Tonga oil field, after the completion of the merger, which is valued at $57bn.
Developed with an estimated investment of $1.3bn, the Caesar Tonga oil field has been in production since March 2012 and is estimated to have a life of 30 years.
The field currently produces at a rate of more than 70,000 barrels of oil per day (bopd), while the recoverable reserves in place are estimated to be up to 400 million barrels of oil equivalent (Mmboe).
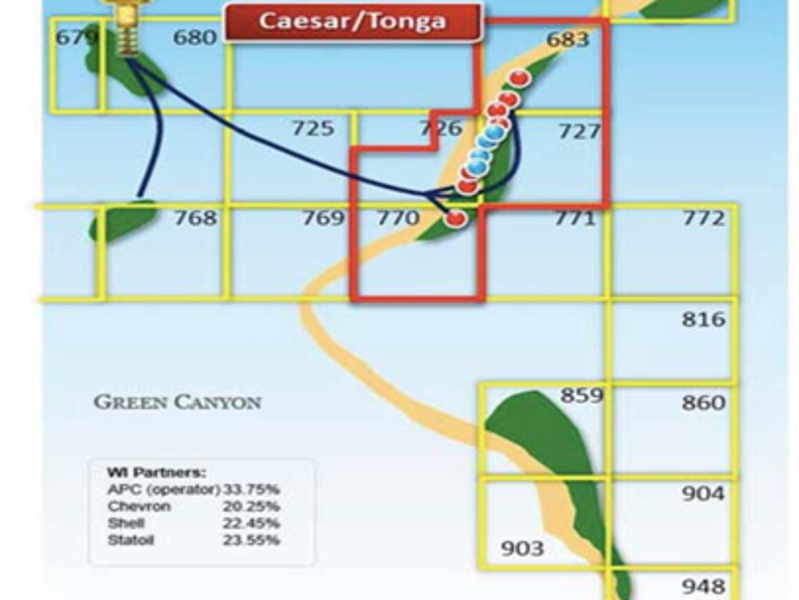
Caesar Tonga oil field location and discovery details
Situated in 1,500m-deep waters approximately 300km offshore of New Orleans, Louisiana, US, the Caesar Tonga oil field complex comprises three discoveries, namely Tonga, Caesar, and West Tonga.
The Tonga field was discovered in 2003, while the Caesar and West Tonga discoveries were announced in 2006 and 2007, respectively.
The offshore oil field complex spans blocks 683, 726, 727, and 770 of Green Canyon area of the US Gulf of Mexico.
Caesar Tonga oil field development details
Caesar Tonga oil field is developed with a total of eight production wells tied-back to the Anadarko-operated Constitution spar platform moored in 4,970ft of water. The wells are connected to the Constitution spar production platforms by two subsea pipelines.
The Caesar Tonga oil field was developed in two phases with each phase involving four production wells.
The initial development works on the field were started in 2007, while the first three development wells were brought on stream at a flow rate of 15,000bopd in March 2012. The fourth development well underwent floor and reservoir tests in the last quarter of 2013.
The remaining four wells were developed in blocks 726 and 727 of Green Canyon starting from 2016, with the last well’s testing completed in the second quarter of 2018.
With 98ft-diameter and 550ft-long hull and 10,770t topside, the Constitution spar platform is capable of producing 70,000 barrels of oil and 200 million metric cubic feet of gas (Mmcf) a day. The oil and gas produced at the platform is transported to Louisiana and Texas coasts.
Contractors involved
Technip FMC was awarded two lump sum contracts for the Caesar Tonga oil field development in July 2009. The scope of the first contract involved the design, supply, and installation of four pipe-in-pipe (PIP) flowlines as well as eight pipeline end terminations (PLETs). Technip carried out the offshore installation works using its deep water pipe-lay vessel Deep Blue.
The second contract, which was awarded to Technip’s subsidiary Duco (now Technip Umbilical), involved the project management, engineering, and assembly of two control umbilicals along with terminal equipment.
Subsea 7 was awarded an engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contract for two manifolds and two riser base pipeline end manifolds in November 2009.
Aspen Aerogels was engaged for the insulation work of the sub-sea tieback of the oil field with the Constitution spar platform.
McDermott International was contracted for the overall project management as well as for the design and installation of two PIP flowlines along with PLETs, one subsea manifold and associated jumpers, and a 72,00ft-long subsea control umbilical for the phase two development of the oil field in January 2016.