The Great Bear Project (previously known as the Dixie project) is a gold property located in Ontario, Canada.
The project is owned by Canada-based gold and silver mining company Kinross Gold Corporation.
In February 2022, the company completed the acquisition of all issued and outstanding shares of Great Bear Resources to buy 100% stake in the gold project.
In aggregate, Kinross paid nearly C$1.35bn in cash and issued approximately 49.3 million Kinross shares and around 59.3 million contingent value rights (CVRs) as consideration.
The company completed a Preliminary Economic Assessment (PEA) for Great Bear Project in September 2024.
According to the PEA, the project has the potential to deliver more than 500,000 ounces annually during the first eight years of its 12-year mine life. LOM average production is expected to be 431koz.
The initial construction capital cost is estimated to be $1.2bn. Around $250m will be invested in mine development before commercial production.
In 2024, Kinross will continue with drilling activity to identify additional open pit and underground opportunities. It is also working on securing necessary permissions on the main project.
Great Bear Project Location
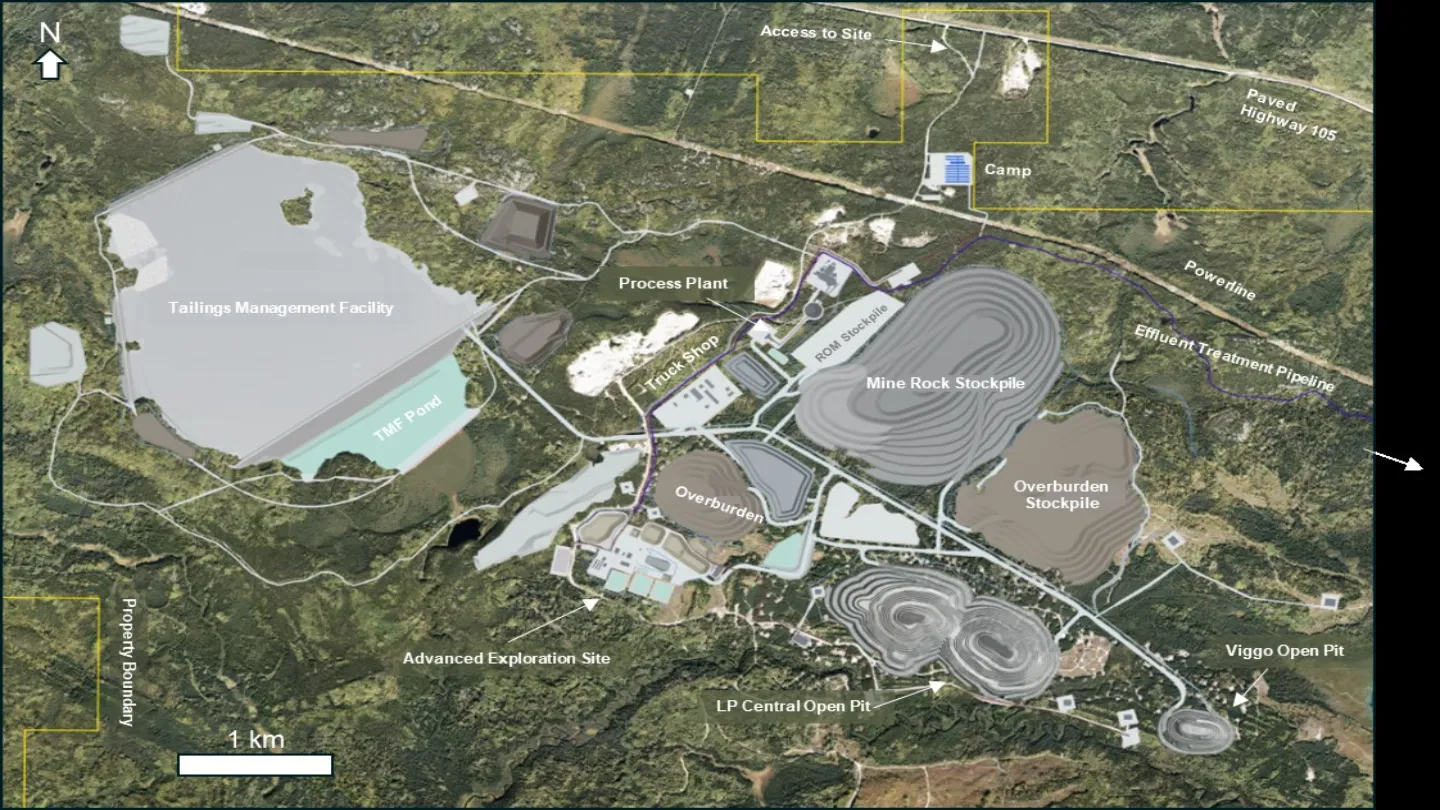
Great Bear Project is located in northwest Ontario, around 24km from the nearest municipality Red Lake.
Overall, the 11,852-hectare property comprises a contiguous block comprising 380 unpatented mining claims and seven mining leases.
Geology and Mineralisation
The gold project is located within the Red Lake greenstone belt, which hosts multiple high-grade Archean mesothermal gold deposits.
Local geology is based geophysics, limited regional scale mapping, and diamond drilling activity.
A regional northwest-southeast trending belt of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks is found within the property area.
The three zones- LP, Hinge, and Limb, feature three dominant styles of mineralisation.
At 800m-long Limb Zone (silica-sulphide replacement), mineralisation is associated with the rheological and geochemical contact between pillow basalt and massive basalt.
Quartz veining – Hinge Zone hosts mineralisation by multiple lithologies including massive basalt (high Mgtholeiite), argillite, and pillow basalt (high-Fe tholeiite), while LP Zone- disseminated gold within high strain – features mineralisation within a wide zone of high strain and increased metamorphic grade.
Great Bear Project Mineral Resource Estimate
The mineral resources at the property were estimated for LP, Hinge, and Limb zones.
As of April 2024, Great Bear’s total Measured and Indicated Resource is estimated to be 30.3 million tonnes at 2.81 grams per tonne gold (g/t Au) containing 2.7 million ounces of gold.
Inferred Resources stand at 25.48 million tonnes at 4.74g/t Au for 3.9 million gold ounces.
Mining and Processing
The PEA outlined simultaneous open pit and underground mining operations over the first eight years. This would be followed by combined underground mining and stockpile processing in the final four years.
The concurrent open pit and underground operations are expected to provide production flexibility and conduct exploration drilling underground to further expand the resource and mine life.
Open pit operations will include one pit phase at the LP Viggo zone and three pit phases at the LP Central zone.
A combined semi-bulk and selective loading unit fleet will be deployed to support mining.
Underground mining will involve longhole open stoping with paste backfill and cemented rock fill (CRF). Underground portals and twin declines will be used to access the underground mine.
Load haul dump (LHD) units and mine trucks on sublevels will haul mined ore to the surface re-handling point.
The combined operation is estimated to produce 44.7Mt of mineralised material producing 5.3Moz of gold.
The average annual gold production is expected to be 482koz from Year 1 to Year 10.
The process plant will be designed to process 10,000tpd of ore. It will comprise the crusher building, stockpile cover, and the process plant building.
The flowsheet includes primary crushing, SAG and ball milling, pebble crushing, gravity concentration, and cyanide leaching followed by carbon adsorption in a carbon-in-pulp (CIP) circuit.
The treated ore will undergo carbon elution, electrowinning, and smelting to produce doré bars.
Key Infrastructure
Great Bear Project can be accessed by an existing forestry road (Tuzyk’s Road) that connects to Highway 105.
The gold project will receive power from the existing 115kV overhead powerline from the Hydro One transmission powerline. A 34.5 kV distribution line will carry electricity to project assets.
The power infrastructure may be further upgraded during the operational phase.
Additionally, an Enbridge natural gas pipeline runs along Highway 105. A branch pipeline will supply natural gas to the project.
Great Bear will procure fresh water from the Chukuni River for operations. It will seek to recycle as much process water as possible.
Other infrastructure will include administration/Dry Building; Truck Shop/Truck Wash Building; Emergency Facilities (medical and fire); Security Gatehouse; Warm and Cold Storage Buildings (warehouses); and Fuelling Station among others.