
A recent H class combined cycle order reported by GE was that from Samsung C&T Corporation, the leader of the engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) consortium that will provide power generation equipment for PetroVietnam Power Corporation (PV Power)’s 1.6 GW Nhon Trach 3 & 4 power plant in Ong Keo Industrial Park, Nhon Trach district, about 70 km southeast of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
This project marks GE’s first H class gas turbine order in Vietnam. Due to enter commercial operation in 2025, Nhon Trach 3 & 4, aka Nhon Trach expansion, will also be Vietnam’s first power plant to be fuelled with liquefied natural gas (LNG).
In addition, a memorandum of understanding aimed at improving the efficiency of the existing Nhon Trach 1 power plant and developing long-term cooperation on the maintenance of Nhon Trach 3 & 4 was signed between GE and PV Power.
Vietnam is currently heavily reliant on coal, which fuels around a third of its electricity output. The growth of gas-fired power generation will support both coal-to-gas transition and also accelerate renewables penetration by enhancing the reliability and stability of the energy grid, says GE, noting that “the project will contribute to the implementation of Vietnam’s announced commitment to achieving net zero carbon emissions by 2050 by supporting the rapid expansion of renewable energy through its dispatchable power profile.”
For each 800 MW block of the Nhon Trach expansion, GE’s scope includes a 9HA.02 gas turbine; an STF-D650 steam turbine; a W88 generator; a once-through heat recovery steam generator; and a Mark* VIe distributed control system.
The new power plant will provide electricity for three large industrial areas in the southern region of Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City, Dong Nai, and Ba Ria – Vung Tau provinces.
“Renewable energy is expected to grow significantly in Vietnam while at the same time, lower carbon and highly efficient gas power generation will play a crucial role in supporting this growth while ensuring grid stability and reliability,” said Ramesh Singaram, president and CEO Asia, GE Gas Power.
“This first-of-its-kind project is expected to open up a new chapter for gas power generation in Vietnam.”
Meanwhile, in Malaysia, the 9HA.02-based 2.2 GW Malacca plant of Edra Energy Sdn Bhd, Malaysia’s second-largest independent power producer, has entered commercial operation.
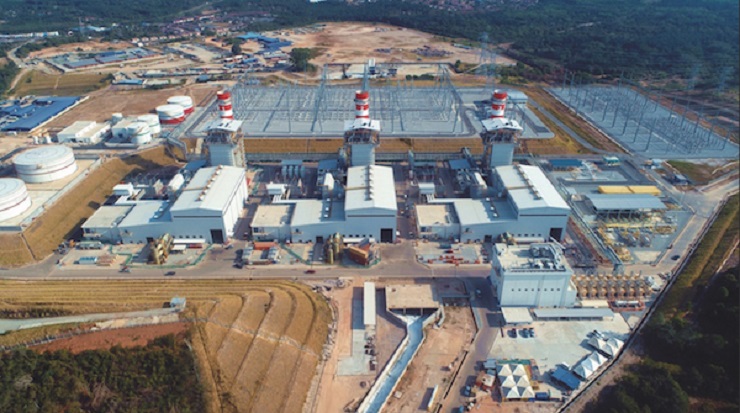

Located in Alor Gajah, it is the largest combined cycle power plant in the country, capable of meeting about 10% of Malaysia’s power demand.
GE says it provided Edra with a holistic solution including a service agreement to manage “all aspects of the project’s lifecycle.”
The new plant consists of three 745 MW blocks, each comprising, as well as the GE 9HA.02 gas turbine: STF-D650 steam turbine; W88 generator; HRSG; and GE Mark* VIe control system. The plant will be equipped with GE Digital’s asset performance management software suite and, in addition, as part of the multiyear services agreement, the power generation equipment at Alor Gajah is monitored by GE’s monitoring & diagnostics centre in Kuala Lumpur.
Edra, Malaysia’s second largest independent power producer, with a focus on gas power generation, is wholly owned by China Solar Energy Investment Ltd, a subsidiary of China General Nuclear Power Corp Ltd.
Total energy consumption in Malaysia continues to increase significantly. According to Energy Watch’s current projections, as cited by GE, Malaysia’s electricity demand is expected to grow from about 18.8 GW in 2020 to over 24 GW by 2039. At the same time, the country’s energy transition objectives in the 12th Malaysia Plan include plans to phase out coal-fired power generation, with an expected 7 GW of coal power to be retired by 2033, leading to a notable increase in demand for other energy sources including gas.
Last year, GE announced the start of commercial operation at Southern Power Generation’s Track 4A power plant, a 1440 MW combined cycle gas power plant in Pasir Gudang, Johor, Malaysia, which also employs GE 9HA.02 technology.
In Thailand, Mitsubishi Power has announced the start-up of a third M701JAC gas turbine unit, part of a project to build two natural gas-fired combined cycle power plants in Thailand.
This is the third of eight single shaft (1×1) units ordered on a full-turnkey basis as part of a joint venture between Gulf Energy Development, one of Thailand’s largest independent power producers, and Mitsui. The first unit, which was also the first M701JAC in Southeast Asia, started commercial operation at the end of March 2021 and the second in September 2021. Both have recorded high availabilities. Mitsubishi Power’s scope includes a 25-year long-term service agreement for these units and provision of O&M support, with remote monitoring of operations via TOMONI, Mitsubishi Power’s suite of “intelligent solutions” that includes an analytical platform which helps optimise power plant operations.
When completed, the eight units will have an installed capacity of 5300 MW.
Construction of the remaining five units is underway and is expected to be completed in 2024, when the final unit starts commercial operation.
The two power plants, each with an installed capacity of 2650 MW, are under construction in Chonburi and Rayong Provinces, approximately 130 km southeast of Bangkok. They will employ natural gas as the primary fuel.
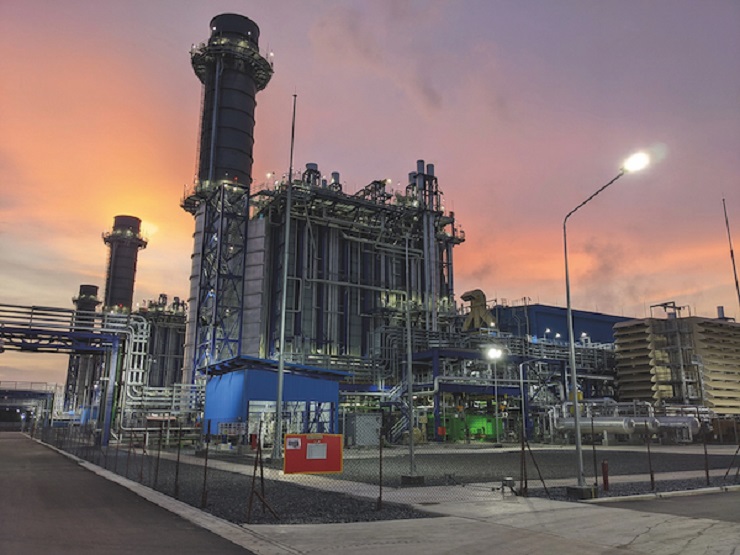

Mitsubishi Power is manufacturing and supplying gas and steam turbines as well as ancillary equipment, while Mitsubishi Electric Corporation is providing generators.
The power generated will be sold to EGAT (Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand).
Mitsubishi reports that its J and JAC series gas turbines have amassed over 1.6 million operating hours to date, with 83 units ordered worldwide.
In China, Siemens Energy has recently entered into agreements separately with Guangdong Energy Group and Shenzhen Energy Group to deliver a total of four H-class combined cycle power units to their power plants located in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) in southern China.
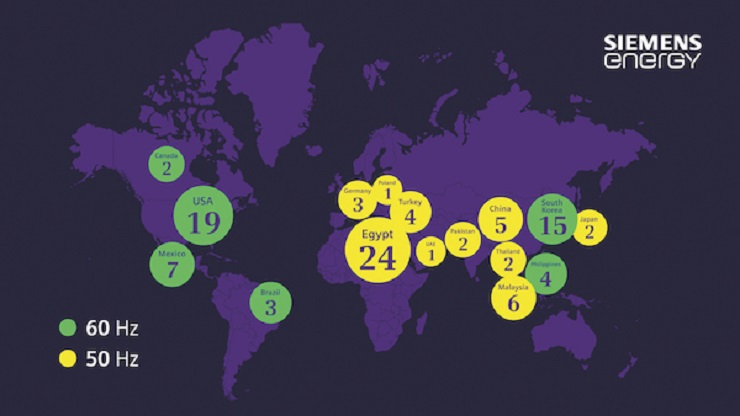
The projects take the number of Siemens SGT5-8000H gas turbines sold to date to 100.
Under the agreement with Guangdong Energy, Siemens Energy will deliver a 675 MW combined cycle plant, including SGT5-8000H gas turbine, steam turbine, two generators and related auxiliary equipment to a site in Guangzhou owned by Guangdong Yuehua Power Co. The existing coal-fired power plant at the site will be transformed into a high-efficiency gas-fired plant.
Siemens will also provide long-term maintenance services.
The agreement with Shenzhen Energy includes supplying three H class combined cycle power units for the Phase II project at the Dongbu power plant and an upgrade project at the Mawan power plant. The scope includes three SGT5-8000H gas turbines, three SST-5000 steam turbines, three SGen5-3000W generators, and auxiliary systems.
The two projects, both located in Shenzhen, are scheduled to go into operation by the end of 2023 and in mid-2024 respectively.
With a population of over 70 million, the GBA is among the most dynamic regions in China. It aims to grow into a global sci-tech innovation centre and provide a role model of sustainable development for the country. In December 2019, Siemens Energy and Shenzhen Energy forged a strategic partnership in the areas of R&D and smart and green energy.
Siemens says there are now 88 SGT-8000H gas turbines in operation on four continents, with over 2.5 million operating hours recorded.
Since launch, the output rating of the gas turbine has grown from 375 MW to 450 MW, with load following capability of 80 MW/minute and combined cycle efficiency of over 62%. The SGT-8000H is also capable of hydrogen co-firing, Siemens notes.
This article first appeared in Modern Power Systems magazine.






