To generate power, a nuclear reactor uses some fissile isotopes that include uranium-235, plutonium-239, and uranium-233. Low-enriched uranium (LEU) is used widely in the nuclear power generation.
Discovered in 1828 by the Swedish chemist Jons Jakob Berzelius, Thorium is a naturally-occurring nuclear fuel source.The isotope uranium-233 produced from thorium is used to generate nuclear fission in a thorium-based nuclear power. Due to its huge potential, thorium as fuel to generate nuclear powe has attracted considerable attention.
Advantages of thorium reactors:
Abundant availability: Thorium is estimated to be available abundantly in the earth’s crust. The vast availability makes it one of the important sources of nuclear fuels. Found in small amounts in most rocks and soils, the slightly radioactive metal is nearly three times more abundant than uranium, according to World Nuclear Association. The IAEA-NEA publication Uranium 2014: Resources, Production and Demand showed the total known and estimated resources of thorium across the world was 6.2 million tonnes.

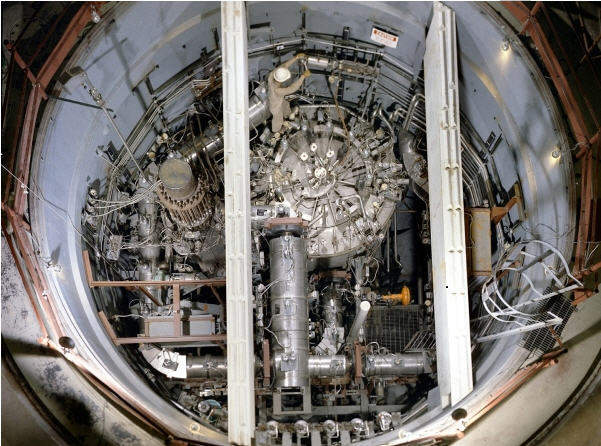
Image: Early thorium-based (MSR) nuclear reactor at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the 1960s. Photo courtesy of Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Suitability: Thorium can be used a nuclear fuel in several types of nuclear reactors that include heavy water reactors, high-temperature gas-cooled reactors, boiling (light) water reactors, pressurised (light) water reactors, fast neutron reactors, molten salt reactors, and accelerator driven reactors.
Checks proliferation: As thorium-based power reactor fuel is a poor source for fissile material that can be used to make an explosive device illegally, proliferation is said to be vastly curtailed by using these reactors.U-233, which is present in the used thorium fuel. It contains U-232 that can lead to a formation a strong gamma radiation field. The creation of such a field enhance the traceability and ability to safeguard the material, thereby addressing the proliferation issues.
Less nuclear waste production: Thorium nuclear power reactors produce less amounts of waste compared to other nuclear fuels. The advantage is one of the key properties of thorium reactors, as the vast amount of nuclear waste created by power plants can lead to high radiation and raise temperature levels.It also avoids a need to have a huge storage facility. Besides, the radioactivity levels of thorium waste are found to fall in a much shorter period than in case of nuclear waste produced by other fuels.

Image: Indian Point Nuclear Power Plant on the Hudson river. Photo courtesy of Tony/Wikipedia.
Safety: Compared to mining of uranium for nuclear fuel, mining thorium is considered as safer and more efficient. Also, thorium’s ore monazite generally comprises significant amounts of thorium, making the element’s extraction cost effective without much impact on the environment. On the other hand, small amounts of uranium can be extracted from its ore. As the mine in case of thorium is an open pit, its mining is found to be safer than uranium mining.
Disadvantages of thorium reactors:
High start-up costs: Huge investments are needed for thorium nuclear power reactor, as it requires significant amount of testing, analysis and licensing work. Also, there is uncertainty over returns on the investments in these reactors. For utilities, this factor can weigh on the decisions to go ahead with plans to deploy the reactors. The reactors also involve high fuel fabrication and reprocessing costs.
High melting point of thorium oxide: As melting point of thorium oxide is much higher compared to that of uranium oxide, high temperatures are needed to make high density ThO2 and ThO2–based mixed oxide fuels. The fuel in nuclear fission reactors is usually based on the metal oxide.
Emission of gamma rays: Presence of Uranium-232 in irradiated thorium or thorium based fuels in large amounts is one of the major disadvantages of thorium nuclear power reactors. It can result in significant emissions of gamma rays.






