China Power Hub Generation Company (CPHGC) has developed a 1.32GW coal-fired thermal power plant approximately 45km away from Karachi in Hub, Balochistan, Pakistan.
CPHGC is a joint venture between Hub Power Company (HUBCO, 74%) and China Power International Holding (CPIH, 26%).
The power project was developed as a part of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), which aims to connect Port Gwadar in southern Pakistan to Xinjiang in China through transportation and energy networks.
The CPHGC power project was proposed in 2015 amongst 51 co-operation agreements that were signed under CPEC. The implementation agreement along with the power purchase agreement for the plant was signed between CPHGC, HUBCO and the government of Pakistan’s Private Power Infrastructure Board in January 2017.
Developed with an estimated investment of $2bn, the coal-fired project is expected to generate nine billion kWh of electricity a year, which will be enough to supply for four million homes in Pakistan.
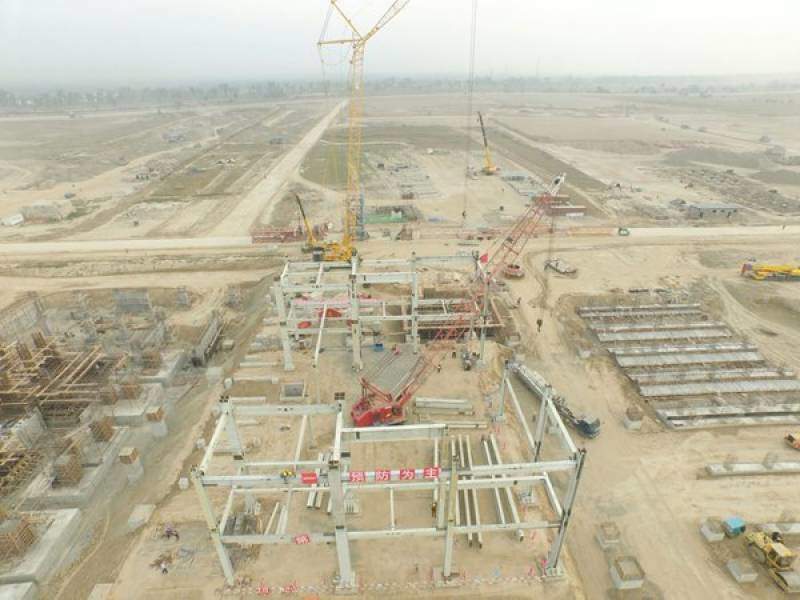
Construction for the power plant began in March 2017, while commissioning took place in 2019.
CPHGC coal-fired thermal power plant make-up
The CPHGC coal-fired thermal power plant has been built on a 1,500-acre site owned by HUBCO and is close to the existing HUBCO oil-fired power plant. It comprises two 660MW super-critical coal-fired boilers units with a main steam temperature of 571°C and pressure of 25.4MPa. Both the boiler units share a double-cylinder flue stack with a height of 210m.
“The CPHGC coal-fired thermal power plant has been built on a 1,500-acre site owned by HUBCO.”
Two single-reheat condensing turbines and two three-phase water and hydrogen-cooled AC generators are also installed at the plant. The generators are connected to a 500kV switchyard through a step-up transformer.
The power plant also includes flue gas control systems to control the NOx emissions, electrostatic precipitators, and distributed control systems. The cooling water system sources water for the power generation from the Arabian Sea, which is located west of the power plant.
Coal supply
The CPHGC power plant is estimated to require 4.185 million tonnes (Mt) of coal a year, which will be imported from either South Africa or Indonesia. The two types of coal planned to be imported include NAR4700 from Indonesia and RB-3 from South Africa.
A coal handling system at the power plant site includes three stockpiles that can meet the plant’s coal needs for a period of 60 days.
Coal handling facilities
A floating jetty has been constructed 5.4km away from the project site at Hub, Lasbella, to import the coal required for the power plant. The jetty is capable of handling carriers with a capacity of 100,000dwt. It features a one-way conveyer belt with a width of 1,800mm and a rated output of 3,600t/h.
A memorandum of understanding (MoU) was signed between Coastal Development & Fisheries Department and CPHGC for the construction of the floating jetty.
Power transmission details
The power generated from the CPHGC coal-fired thermal power plant will be fed to the national grid operated by Pakistan’s National Electric Power Regulatory Authority (NEPRA).
A 500kV, 220km double-circuit transmission line connects the plant to NEPRA’s Matian switching/convertor station for transmission to the grid.
Financing for CPHGC coal-fired thermal power plant
A consortium of Chinese banks led by China Development Bank provided $1.5bn or 75% of the total construction cost of the power plant under a Foreign Loan Facility Agreement signed with CPHGC in October 2017.
Contractors involved
The engineering, procurement and construction contract (EPC) for the power plant was awarded to a special consortium between Northwest Electric Power Design Institute (NWEPDI) and TianJin Electric Power Construction (TEPC) in May 2016.
General Electric was contracted by the NWEPDI-TEPC JV for supplying two steam turbines, boilers, and generators for the power plant in March 2017.
The operation and maintenance contract for the project was awarded to a consortium of China Energy Engineering Group, TEPC, CEEC Tianjin (Pakistan), Electric Power Construction, China Energy Engineering Group Science and Technology Development in April 2018.