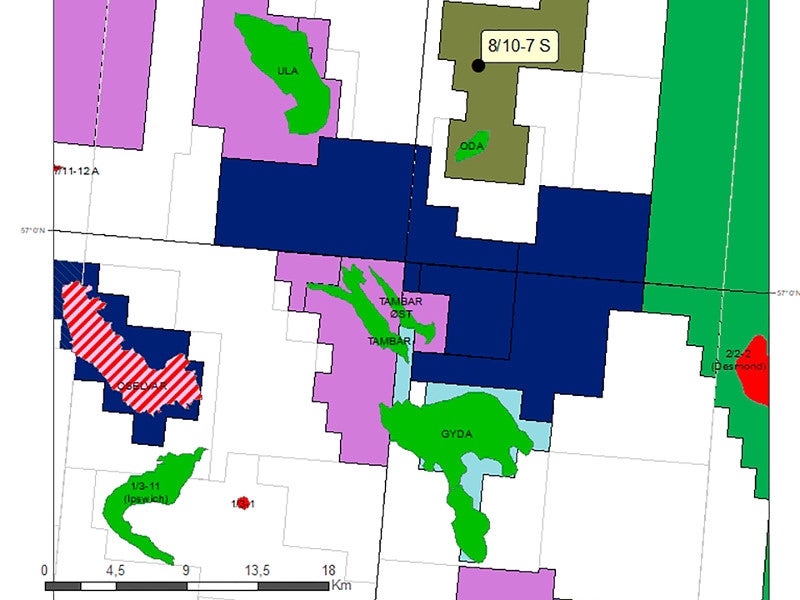
Oda is an offshore oil and gas field located in the southern part of Norwegian North Sea. Developed as a subsea tie-back to the Ula production platform located approximately 13km to the east, the Oda field was brought on stream in March 2019.
Oda is one of the two producing fields being operated by Spirit Energy Norway in the Norwegian North Sea. Spirit Energy Norway is a subsidiary of Spirit Energy, a joint venture between Centrica (69%) and Bayerngas Norge (31%).
Spirit Energy Norway holds 40% interest in the Oda field, while the remaining stakes are held by Suncor Energy Norge (30%), DNO North Sea (15%), and Aker BP (15%).
The field was developed with an estimated investment of £478m ($633m).
Reserves and production
The recoverable reserves of the Oda field are estimated to be approximately 33 million barrels of oil-equivalent (Mboe), containing 5.04 million cubic metres of oil and 0.21 million cubic metres of gas.
The field is expected to produce up to 35,000 barrels of oil-equivalent per day (boed).
Oda field location, discovery, and reservoir details
The Oda field is located in 65m-deep waters in block 8/10 and encompasses 71km² of the production license 405 in the Norwegian Continental Shelf (NCS), which is valid up to 2036.
Originally named as the Butch field, the Oda offshore field was discovered by the 8/10-4 S wildcat exploration well in October 2011. It was further appraised by the 8/10-4 A appraisal well in December 2011.
The reservoir of the field is located 2,900m below the seabed and forms part of the Ula sandstone formation of the late Jurassic age.
Oda field development details
Centrica submitted the plan for development and operation (PDO) of the Oda field in November 2016 and the same was approved by Norway’s Ministry of Petroleum and Energy in May 2017.
The field is developed with a four-slot seabed template with two production wells tied-back to the Ula field and one water injection well to provide pressure support for enhanced oil recovery. The development drilling was completed between August and October 2018.
The well stream of the field is processed at the Aker BP-operated Ula production platform situated in 70m-deep waters.
The Oda field’s tie-in with the Ula platform involved the reuse of the processing equipment and hook-up infrastructure for the Faroe Petroleum (now DNO North Sea)-operated Oselvar field, which was shut down in May 2018.
The Oda field’s oil output from the Ula platform is first sent to the Ekofisk field and further exported via the 20in-diameter Norpipe to the Teesside terminal in the UK.
The gas produced by the Oda field is injected into the Ula reservoir to improve oil recovery at the Ula field, which has been in production since 1986.
Contractors involved
Spirit Energy signed long-term strategic contracts with Aibel, Subsea 7, TechnipFMC, and maritime classification company DNV GL for the development of the Oda field in 2016.
TechnipFMC provided the subsea production structure, while Aibel supplied the subsea manifold. Subsea 7 supplied the subsea umbilicals, risers, and flow lines (SURF) for the project.
DNV GL engaged First Ocean Associates for marine warranty survey for the Oda field development in March 2018.