The Panki extension project involves the expansion of the existing Panki thermal power station’s (TPS) capacity from 210MW to 660MW. The project will be located in the premises of existing Panki TPS, approximately 16km from Kanpur, Uttar pradesh District of India.
The plant will be developed as a lignite-fired, supercritical thermal power plant with a net output of 660MW. It is expected to start generating power during the 13th Plan period (2017-2022).
Uttar Pradesh Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam (UPRVUNL) is the project developer.
Environmental clearance (EC) for the project was granted in 2017. The construction is estimated to take 46 months for completion. The plant is expected to start electricity generation in January 2022.
Panki extension project make-up
The existing Panki thermal power station consists of two 105MW coal-based power units, which were derated from 110MW. Two 32MW power units at the plant were closed, while the two 105MW units too will be decommissioned in phases, following the commissioning of the new 660MW unit.
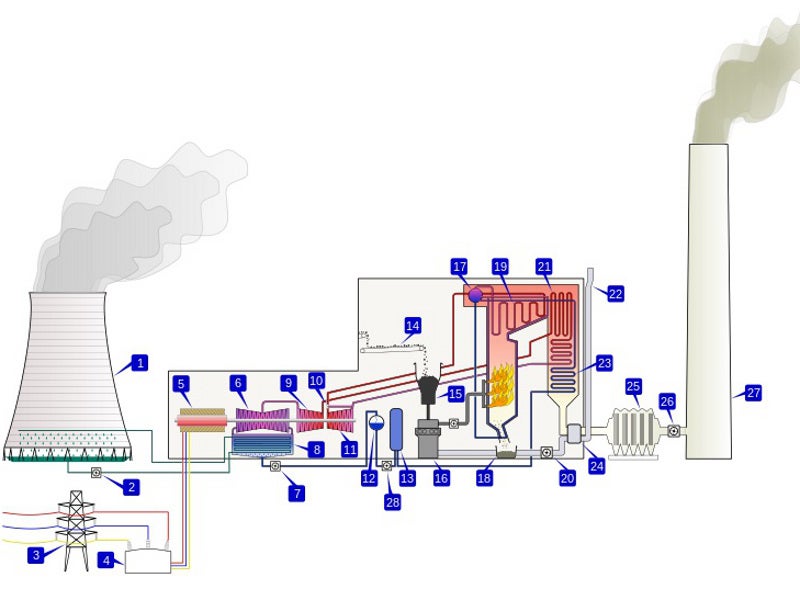
The expansion project will involve the installation of an electro-hydraulic steam turbine and a deaerator. The turbine will have three main parts – a single-flow high-pressure (HP) section, a double-flow intermediate-pressure (IP), and a low-pressure (LP) section.
Individual shafts of the cylinders will be rigidly coupled with the generator rotor shaft.
The high-pressure turbine will be a single flow type and will comprise two casings – an inner casing carrier and a barrel type outer casing. Steam will be supplied to the HP turbine by using two combined stop and control valves.
The double-flow IP turbine will have a double-shelled casing system with horizontally split inner and outer casings. Reheat steam is injected through stop and control valves of the turbine, while the exhaust branches will be located on top of the casing.
The low-pressure turbine will have a horizontally split multi-casing, with bearing pedestals mounted on the foundation.
The generator will be a three-phased, horizontally mounted, and two-pole cylindrical rotor type. It will be directly driven by steam from the steam turbine, which operates at a rated speed of 3,000rpm.
The project will also include the addition of two turbine-driven and one electric motor-driven boiler feed pumps, with booster pumps mounted on a common shaft. The boiler feed pumps will be of horizontal, centrifugal type with shaft.
A pressure conveying system will be used to convey the fly ash generated by electrostatic precipitator (ESP) hoppers to fly ash silos. It will be further disposed in dry form through trucks or in wet form to ash disposal area through high concentrated slurry disposal (HCSD) system.
Transmission and off-take of power
The power generated by the supercritical power plant will be evacuated to the grid through two single-circuit 400kV lines. Two outgoing line bays and two receiving bays will be used for the same.
A new 400kV switchyard, comprising two main and one transfer-by switching schemes, will be constructed at the Panki power station. It will include a generator transformer bay, two outgoing line bays, one station transformer bay, and a bus coupler bay.
A short transmission line will be used to connect the two outgoing line bays with the nearby Uttar Pradesh Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam (UPPTCL) 400kV substation.
Uttar Pradesh will receive the entire power generated by the Panki extension project, while the surplus power, if any, will be fed to the Northern Grid for supply to other northern states.
Fuel supply for Panki extension project
The Panki extension project is expected to require approximately 2.76 million tons per annum (Mtpa) of coal, which will be sourced from the coal blocks of Saharpur-Jamarpani Sector, Brahmani Basin, and Rajmahal group of coalfields in Dumka district of Jharkhand.
Contractors involved
UPRVUNL awarded the engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contract, worth Rs44bn ($633m), to Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) in March 2018.
BHEL proposes to engage its Northern Region division for the construction and installation activities, while the key equipment will be manufactured at its plants in Trichy, Haridwar, Hyderabad, Ranipet, Bhopal, Bengaluru, and Jhansi.