The San Dimas Silver-Gold Project is an operational underground gold-silver mine located in the State of Durango in Mexico.
The project is 100% owned by First Majestic Silver, a Canada-based mining company focused on silver and gold production in Mexico and the US. It is operated by the company’s indirect wholly owned subsidiary Primero Empresa Minera.
In 2023, the silver-gold project produced 26.9 million AgEq ounces, comprising 10.3 million silver ounces and 198,921 gold ounces.
First Majestic has a long-term mine and mill optimisation plan for future.
In June 2024, the company announced positive drilling results from its 2024 exploration programme at tested new silver and gold mineral targets.
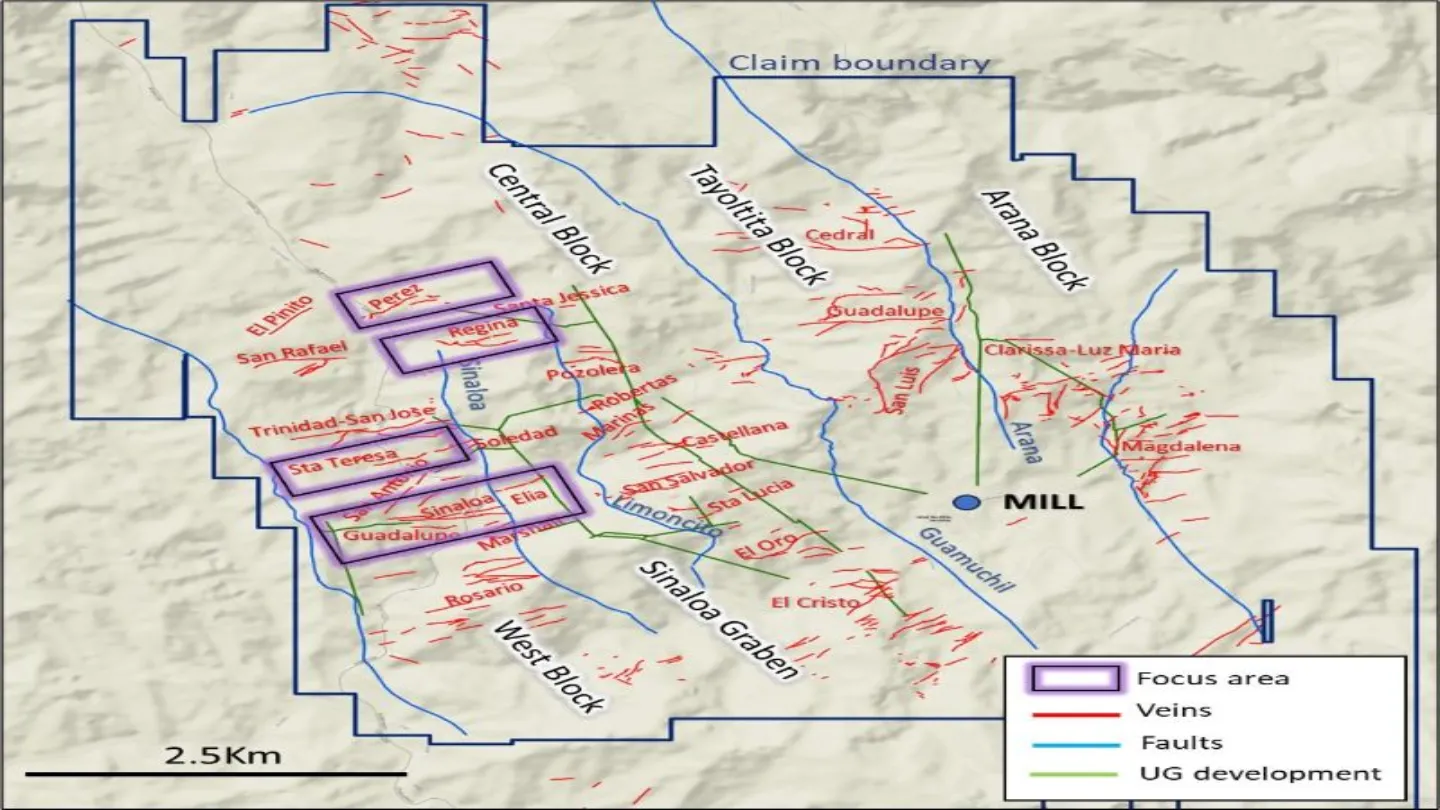
San Dimas Project Location
The San Dimas Silver-Gold Project is located on the borders of Durango and Sinaloa near Tayoltita Town in the San Dimas District. The project lies approximately 150km west of the city of Durango and 125km northeast of Mazatlán.
The property consists of 119 mining concessions spread over 71,867 hectares (ha). The area is divided into six concession groups- the San Dimas, Candelero, Ventanas, Lechuguillas, Cebollas and Truchas.
The project is accessible by air and road from Durango, Mazatlán, and Tayoltita.
San Dimas Project Ownership and Production History
The region has a record of mining activity in 16th and 17th centuries.
Mining activities ceased during the Mexican War of Independence, with minor mining continued from 1821 to 1880.
William Randolph Hearst acquired the Tayoltita Mine under San Luis Mining in 1880. This restarted the mining activities in the area.
The San Dimas properties were consolidated in 1941.
In 1961, Minas de San Luis, owned by Mexican interests, purchased 51% of the properties and operated the mine in partnership with San Luis Mining from 1962 to 1977.
Wheaton River Minerals became the owner of the operations in 2002, following a series of ownership changes. In 2003, the production rate of the mine increased to 1,600tpd.
Wheaton merged with Goldcorp in 2005 and the production of the mine increased to 2,100tpd.
The mine was acquired by Mala Noche in 2010.
Mala Noche changed its name to Primero Mining in 2011. Primero operated the mine from 2011 to 2018 achieving a peak production of 2,800tpd in 2016.
Primero acquired interest in the Lechuguillas Concessions Group to increase the land position between 2011 and 2018.
In 2018, First Majestic acquired the project by purchasing Primero. The streaming contract with Wheaton Precious Metals was renegotiated.
During 2019-2020, average production rate at the San Dimas Mine was 1,975 tpd.
Geology and Mineralisation Details
The San Dimas Silver-Gold Project lies in the central Sierra Madre Occidental (SMO) mountain range. It consists of Late Cretaceous to Early Miocene igneous rocks including two major volcanic successions.
The Lower Volcanic Complex (LVC) consists of andesitic and rhyolitic flows and tuffs, while the Tertiary aged Upper Volcanic Group (UVG) lies above LVC and includes a lower andesitic horizon capped by rhyolitic ash flows and tuffs.
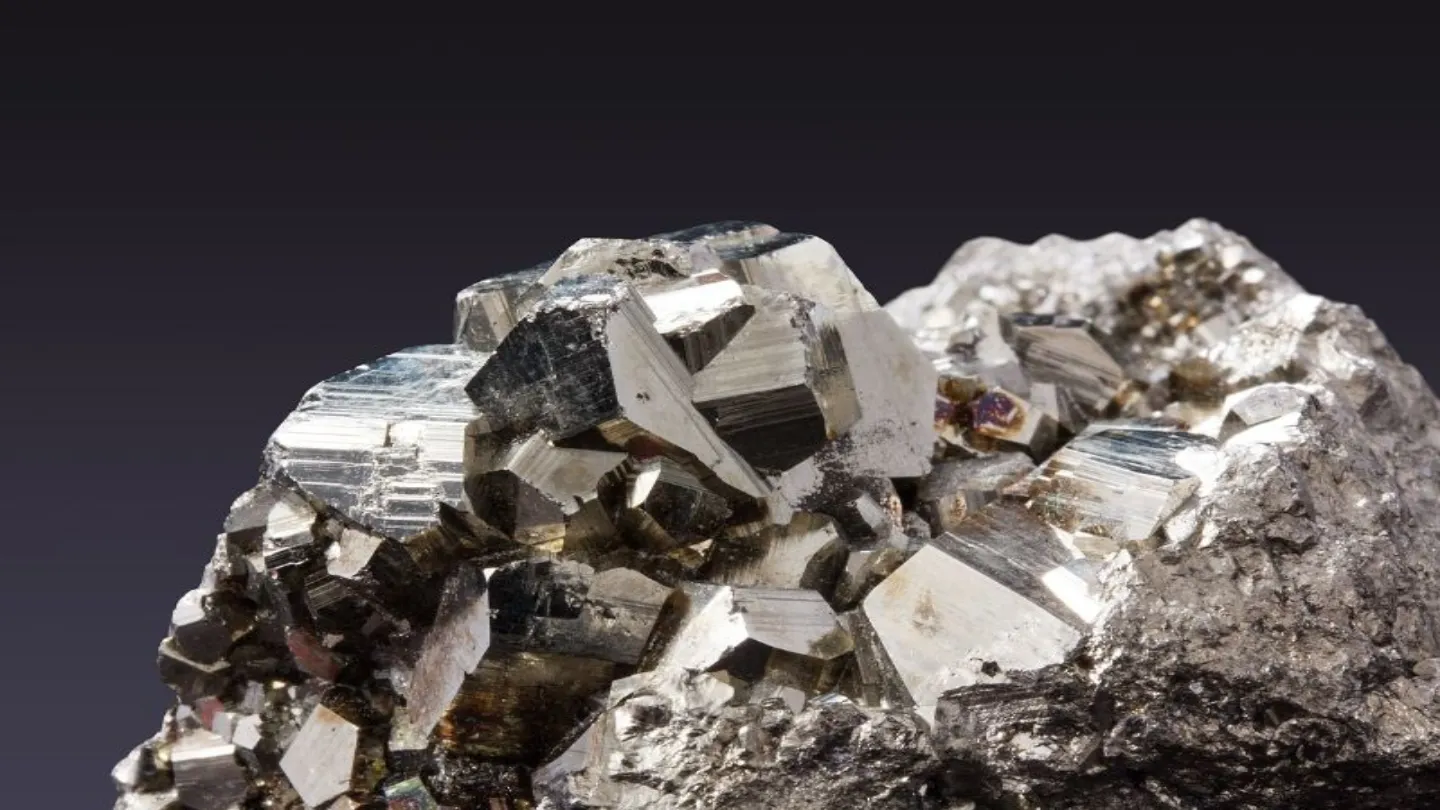
Precious metal ore is found in more than 120 epithermal veins featuring low sulphidation and adularia-sericitic alteration. The widths of the veins vary from less than 1cm to over 15m with an average of around 2m.
According to the technical report, mineralisation is typical epithermal vein structures with banded and drussy textures.
There are three major stages of veining identified, each hosting different amounts of mineralisation.
The second stage produces the maximum of ore deposits. It includes three sub-stages- quartz-chlorite-adularia, quartz-rhodonite and quartz-calcite. Sulphide minerals that are primarily found include pyrite, sphalerite, chalcopyrite and galena.
The ore deposits are usually found within the ‘Favourable Zone’.
San Dimas Project Reserves
As of December 2020, the gold-silver mine is estimated to contain 3.99Mt of proven and probable reserves containing 42.3Moz of silver at a grading of 330g/t Ag and 484,000oz of gold at 3.77g/t.
Total measured and indicated mineral resource estimate is 4.5Mt containing 62.6Moz of silver and 753koz of gold.
San Dimas Inferred Mineral Resource Estimate is 5.5Mt containing 60.3Moz of silver and 642koz of gold.
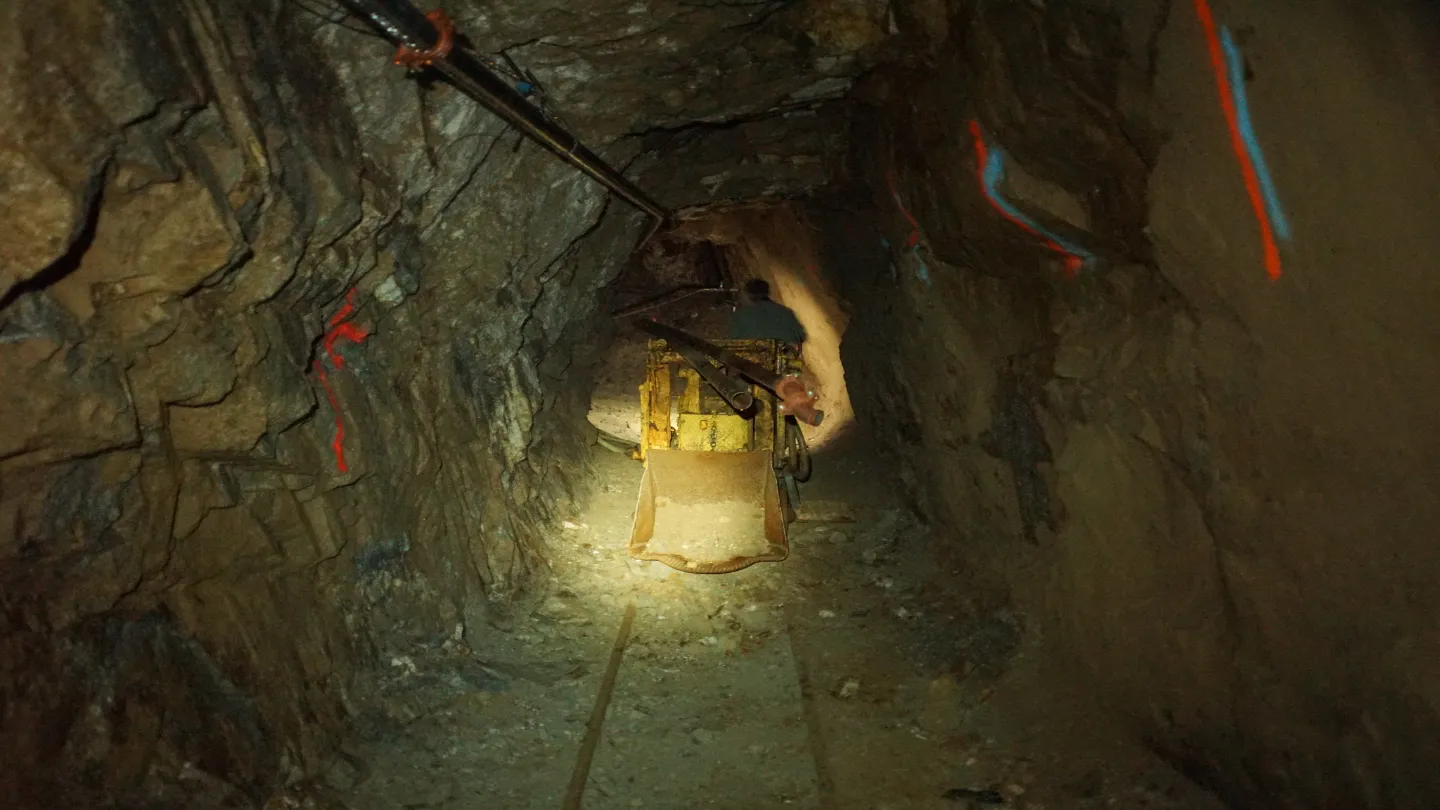
Mining and Processing Methods
The San Dimas mine features five underground gold and silver mining areas- West Block (San Antonio mine), Sinaloa Graben Block (Graben Block), Central Block, Tayoltita Block, and the Arana Hanging-wall Block (Santa Rita mine).
The project is mined using cut-and-fill and long-hole stoping methods. Cut-and-fill is done by either jumbo or jackleg drills, while long-hole stoping is conducted by pneumatic and electro-hydraulic drills.
The processing of ores is conducted by a 2,500tpd processing plant in Tayoltita.
This includes cyanide tank leaching and Merrill-Crowe of ground plant feed for producing gold and silver doré bars.
The plant consists of a single train with a separate crushing part. The train is connected to the fine-ore bins through a belt conveyor.
Other circuits of the plant are grinding, leach tanks, Counter Current Decantation (CCD) tanks, Merril-Crowe, smelting, and tailing filtration and stacking.
Metal recoveries were estimated to be 94% for silver and 96.5% for gold.
San Dimas Project Infrastructure
The project has a well-developed infrastructure consisting of access roads, mines, the Tayoltita mill, an assay laboratory, the Cupias/Tayoltita tailing facilities, a stamp camp, and offices.
The Las Truchas hydroelectric generation system, a diesel-powered emergency generation plant, a local airport, and support facilities for the inhabitants of Tayoltita are also used.
Water for the industrial use is sourced mainly from the recycled filtered tailing water from mine dewatering stations after treatment.
Power is supplied by the Las Truchas hydroelectric generation system and the CFE supply system. Both systems are owned by First Majestic.
A few backup diesel generators are used in emergencies. The Las Truchas has been equipped with two 60 generators with a capacity of over 60 gigawatt hours (GWh) per year since 2015.
The construction of an 18 million cubic metre (Mm3) second water storage dam is being assessed by First Majestic. The dam would feed the Las Truchas and increase its electricity generating capacity.
Contractors Involved
The 2014 technical report of the project was prepared by Primero Mining and AMC Mining Consultants (Canada).