The Santa Fe Project is a gold-silver mine located in the Mineral County, Walker Lane district of Nevada, the US. It is expected to be mined using conventional open pit methods.
Lahontan Gold, a Canadian gold and silver exploration company, is the 100% owner of the project via its wholly owned subsidiaries Gateway Gold (USA) and Lahontan Gold (US).
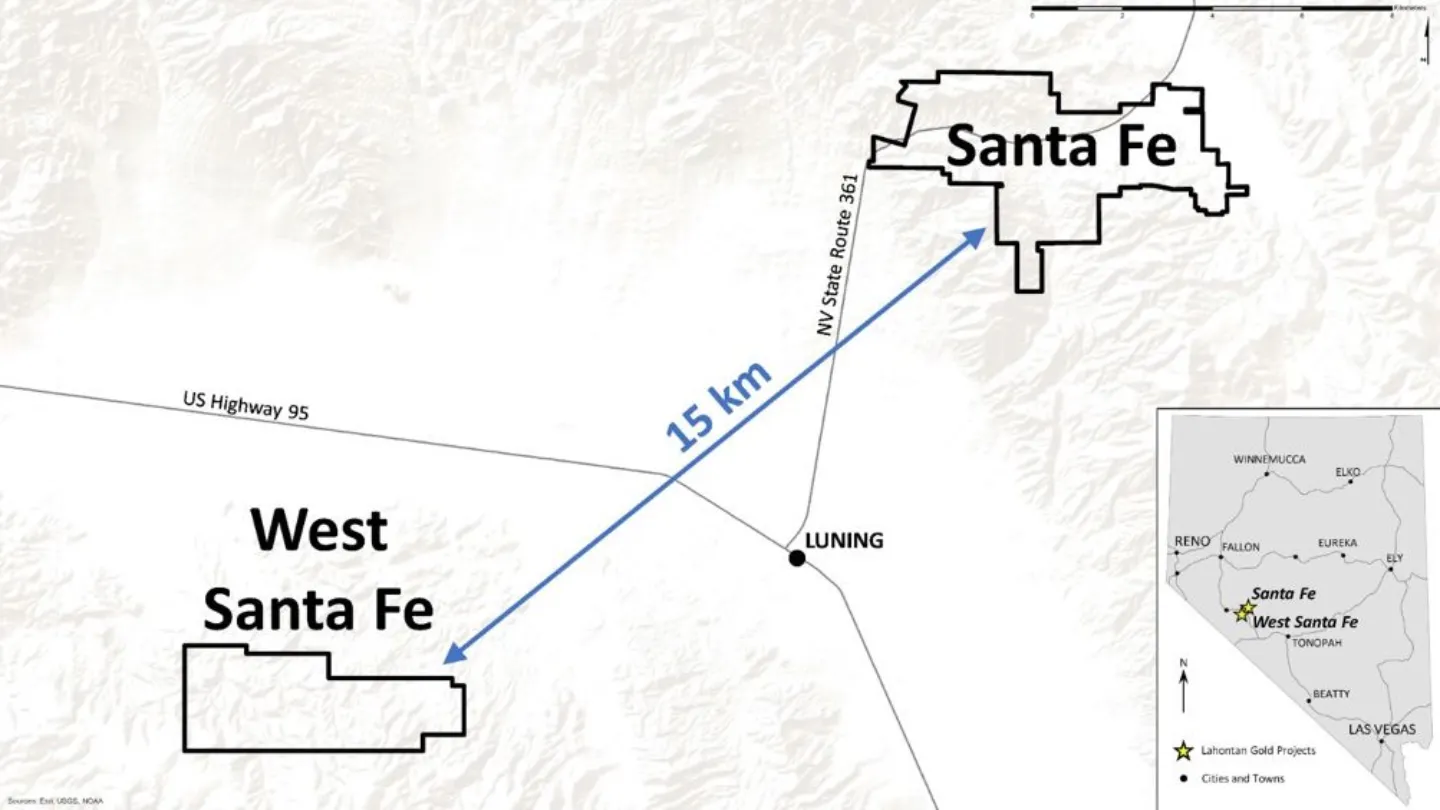
The property consists of east and west portions. The east portion comprises the Slab, Calvada East, and York deposits. The west portion consists of the Santa Fe deposit.
In June 2024, the first and second phase of drilling were successfully concluded using MPD-1500 rig.
The Preliminary Economic Assessment (PEA) reported in January 2025 outlines a total (pre-production + sustaining) capital cost of $152.9m, a processing rate of approximately 12,500 tonnes per day (tpd) over 6.14 years of Life of Mine (LOM).
Santa Fe Project Location
The Santa Fe Project is located 176km southeast of the city of Reno and approximately 10km northeast of the town of Luning within the Santa Fe Mining District in the Basin and Range Province.
The project consists of 388 unpatented claims, 67 patented millsite claims, and 24 patented mining claims covering 26.4km2.
The mine is accessible by a paved state road crossing the property. The site can be reached from the town of Hawthorne.
Numerous gravel haul roads, access roads, and drill roads cross the project site.
Ownership History
The east portions of the property were held by a joint venture between CoCa Mines and Amax Gold.
The portions were purchased by Corona Gold in 1989. Before the joint venture, exploration is not known.
The west portion was staked by Cordero Mining in the early 1960s. Cordero optioned it to Callahan Mining who dropped the option later.
Cordero optioned the property in 1971 to Bell Mountain Silver Mines who optioned it to Bethlehem Mines in 1974.
The property was reverted to Westley Mines until 1978 when it was optioned to Inco. Inco dropped the option, and the property went back to Westley until 1979 when Ventures West Minerals bought the property.
In 1983, Ventures West formed a three-way joint venture with Brican Resources and Lancana Gold.
Lancana consolidated the joint venture in 1986 and became the sole owner of the property.
Corona Gold purchased Lancana in 1989 and merged with Homestake Mining in 1992. Homestake became the owner of the project.
In 2001, Homestake merged with Barrick Gold who owned the project until 2008 when Gateway optioned the project.
In 2008, Gateway merged with Victoria Gold who assumed the option agreement between Gateway and Barrick.
Victoria entered into a definitive purchase and sale agreement in 2012 with a wholly owned subsidiary of Barrick to sell Victoria’s interest in the Mill Canyon Property as the 2008 option agreement failed.
Victoria received Barrick’s rights, title, and interest in Santa Fe.
In 2020, Victoria sold Gateway’s subsidiary to Lahontan and became the 100% owner of the project.
Geology and Mineralisation
The gold and silver deposits at the mine were deposited from epithermal hydrothermal systems and were formed during Cenozoic volcanism along the Cascade Arc.
The arc is a volcanic belt formed from eastward subduction of the Farallon plate beneath North America.
The epithermal systems are strongly structurally controlled as gold and silver transporting fluids in these are hosted within faults and fractures.
The system and arc rocks are superimposed upon the existing basement rocks. Both basement and unconformably overlying volcanic rocks host gold and silver deposits.
The basement rocks consist of mainly medium to thickly bedded limestone, lesser dolomite, and siliciclastic rocks of the Triassic Luning Formation.
The stratified rocks of the formation is intruded by Jurassic or Cretaceous diorite stocks, dykes, and Cretaceous quartz, monzonite, and granite.
The Oligocene to Miocene ash flow tuff contains minor lava deposits up to 1,000m and overlie the older basement rocks.
The gold and silver mineralisation is controlled by several faults, lithological contrasts, fault intersections, and fault jogs.
Santa Fe Project Mineral Resource Estimate
The indicated mineral resource estimate for the project is 48,393kt containing 1,439koz gold at a grading of 0.92g/t and 11,177koz silver at a grading of 7.18g/t, and 1,539oz gold equivalent (AuEq) at a grading of 0.99g/t.
The inferred mineral resources for Santa Fe are 16,760kt containing 401koz gold at a grading of 0.74g/t, 1,749koz silver at a grading of 3.25g/t, and 411oz gold equivalent at a grading of 0.76g/t.
Mining and Recovery Methods
From the Santa Fe Project, mining will be conducted using conventional open pit truck and loader methods.
A total of 16-haul trucks, 3 loaders, e production drills, 2 pioneer/pre-split drills, and a fleet of graders, water trucks, and other equipment have been assumed by RESPEC in the PEA.
Using 100-tonne haul trucks, the waste material will be mined and transported to the waste rock storage facilities.
The leach material will be mined from the pit and processed by a crusher and then stacked on a heap leach pad to leach gold and silver.
The mineralised heap leach material will undergo a three-stage crushing in process plant to produce a P80 12.7mm product.
The product will be conveyed to a conveyor stacking with a radial retreat stacker and then to conventional heap leaching circuit with dilute sodium cyanide solution.
Gold and silver will be recovered by carbon -in-columns using carbon adsorption.
Using pressure elution and carbon reactivation, desorption of gold and silver will occur by acid washing and kiln regeneration.
Electrowinning will precipitate gold and silver from eluate. This will be followed by mercury retorting and smelting to produce doré bars.
Santa Fe Project Infrastructure and Power Supply
The infrastructure of Santa Fe includes access roads, buildings, site water balance facilities, water supply and distribution facilities, explosive storage facilities, security, and waste disposal facilities.
The project will receive power at 120kV from the main Santa Fe Substation owned by NV Energy, a public utility company, via overhead transmission lines. The substation will be located near the administration area of the project.
The substation will step down voltage and supply to the site distribution line.
Contractors Involved
The PEA for the Santa Fe Project was prepared by USA engineering consultants Kappes, Cassiday & Associates (KCA) and RESPEC, Canadian mining consultant Equity Exploration Consultants, and USA environmental consultant Great Basin Environmental Services.
KCA conducted metallurgical testing for the project. The testing commenced in July 2024.
In March 2021, Lahontan contracted a USA based geophysical survey provider Zonge Geoscience for an airborne drone magnetic survey on around 19.5km2.